如何管理多模块工程中的依赖?
如今,Android 应用程序的模块化已成为 Android 社区中的热门话题。每个模块的依赖性管理比以往任何时候都变得越来越重要。
通过阅读本文,您将学会使用不同的方法来管理项目的依赖关系:使用根项目的 ext 块,或通过在模块中引用包含依赖关系的独立文件中的依赖,或使用 buildSrc 模块管理依赖。
1. 使用 ext 块
我们需要在项目的 build.gradle 中定义所需的依赖项,以使该变量可以在所有子模块中访问
buildscript {
ext {
kotlin_version = '1.3.11'
appcompat_version = "28.0.0"
junit_version = "4.12"
test_runner_version = "1.0.2"
}
} 我们在 buildscript ext 块中定义了必需的依赖库版本,并更新模块的依赖关系为此处的版本变量。
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:$kotlin_version"
implementation "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:$appcompat_version"
testImplementation "junit:junit:$junit_version"
androidTestImplementation "com.android.support.test:runner:$test_runner_version"
}总结: 这种方式非常简单明了,支持版本更新检查提示,可以方便的管理和维护。仅在单一项目中集成很合适,但是要在多个工程中共享依赖版本则需要拷贝 ext 块。
2. 从单独文件中引用
这个方法与上一个方法类似,但看起来更为简洁,因为所有依赖项和版本均从单独的文件中引用。
可以参考 dependencies.gradle 文件,我们新建一个 dependencies.gradle 文件:
ext {
kotlinVersion = '1.3.11'
appCompatVersion = "1.1.0"
constraintLayoutVersion = "1.1.0"
junit4Version = "4.12"
testRunnerVersion = "1.2.0"
libraries = [
kotlinStdLib : "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:" + kotlinVersion,
appCompat : "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:" + appCompatVersion,
constraintLayout: "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:" + constraintLayoutVersion
]
testLibraries = [
junit4: "junit:junit:" + junit4Version
]
androidTestLibraries = [
testRunner: "com.android.support.test:runner:" + testRunnerVersion
]
}buildscript {
apply from: 'dependencies.gradle'
}在项目 buildscript 块中的 引用 dependencies.gradle 文件,以便所有模块可以访问依赖变量,并使用依赖变量更新子模块的依赖关系。
dependencies {
implementation libraries.kotlinStdLib
implementation libraries.appCompat
testImplementation testLibraries.junit4
androidTestImplementation androidTestLibraries.testRunner
}总结: 这种方式可以隐藏在模块中依赖的版本细节,同时 apply from 方式引入 ext 块,可以将文件托管到网络上并从网络引入,可以方便的跨多个工程统一管理依赖版本,但是不能很直观的理解,不支持版本更新提示。
3. 使用 buildSrc
通过这种方法,我们可以在所有模块的 build.gradle 文件中使用代码补全。我们可以在项目结构里使用 Kotlin 或 Java 来定义和管理依赖项。
使用 Java
首先,我们需要在项目的根目录中创建 buildSrc 目录。如果要使用 Java,则需要创建 src/main/java/Dependency 类并定义依赖项。
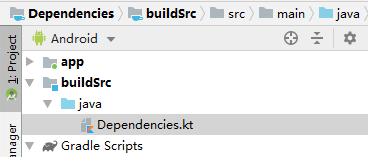
我们将类命名为Dependencies,但是您可以根据需要随意命名。
public class Dependencies {
public final static String APP_COMPAT_VERSION = "1.1.0";
public final static String KOTLIN_VERSION = "1.3.41";
public final static String APP_COMPAT = "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:" + APP_COMPAT_VERSION;
public final static String KOTLIN_STDLIB = "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:" + KOTLIN_VERSION;
}然后,在模块 build.gralde 文件中添加依赖关系:
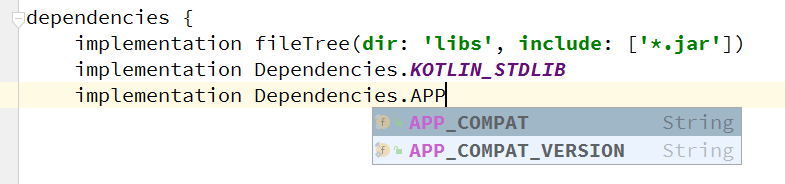
使用 Kotlin
我们需要在项目的根目录中创建 buildSrc 目录,并在 buildSrc 目录中创建 build.gradle.kts。然后在 build.gradle.kts 中附加 kotlin-dsl 插件。
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}
repositories {
jcenter()
}import Versions.APP_COMPAT_VERSION
import Versions.CONSTRAINT_VERSION
import Versions.KOTLIN_VERSION
object Versions {
const val APP_COMPAT_VERSION = "1.1.0"
const val KOTLIN_VERSION = "1.3.41"
const val CONSTRAINT_VERSION = "1.1.0"
}
object Dependencies {
val APP_COMPAT = "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:$APP_COMPAT_VERSION"
val KOTLIN_STDLIB = "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:$KOTLIN_VERSION"
val CONSTRAINT_LAYOUT = "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:$CONSTRAINT_VERSION"
}最后,从 Deps 对象中引用依赖:
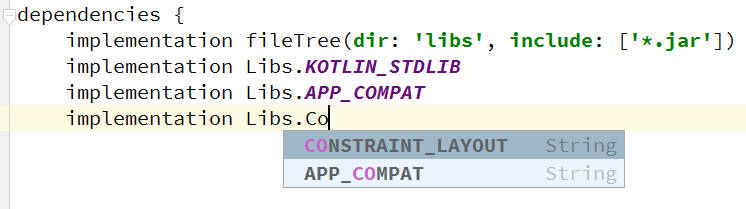
总结: 这种方式可以在代码中很方便的集中管理依赖关系,简单易懂,支持点击跳转和自动补全。但是不支持版本更新检查,也不能方便的跨项目使用,可以通过 git submodule 的方式跨项目使用。
使用场景
对于这三种方式,如每一个小结的总结,各有利弊,可以分为如下几个使用场景:
1. 如果考虑到版本更新提示,则方式一 ext 块最佳;
2. 如果不考虑版本更新提示,需要跨项目管理,则方式二独立文件最佳;
3. 如果不考虑版本更新提示,需要自动补全和点击跳转,则方式三 buildSrc 最佳;
4. 如果不考虑版本更新提示,需要自动补全,且需要跨项目管理,则可以使用方式三 buildSrc 搭配 git submodule 管理;
5. 如果考虑到版本更新提示,且需要跨项目管理,则可以仅在方式二独立文件中包含版本号信息,并托管到远程服务上,只统一管理版本号更新;
6. 如果需要版本更新提示,且需要自动补全,对不起,目前还没有方法;
7. 如果您既要版本更新提示,又要跨项目管理,又要自动补全,对不起,目前还没有方法,您可能需要自己编写插件来支持。当然您也可以单独创建一个工程,结合场景4和场景1共用版本号,同时可以使用 ci 每天自动编译通过 Lint 检查版本更新,有更新时手动或写脚本自动提交更新。